Internal vs external auditing

However, for those who like to be part of an ongoing endeavour in a team environment, internal audit is a more appealing career choice. From a career perspective, both internal audit and external audit offer up some really interesting opportunities. Which direction you choose to take really depends on your own strengths and preferences.
Advisory and Consulting Services
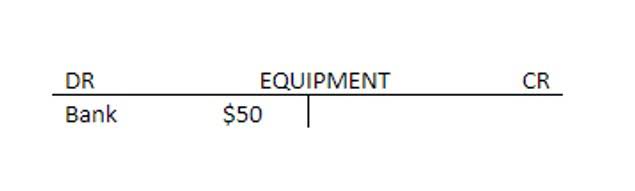
- Internal audit is one of the sectors of an organization that ensures independent review and unbiased process of the system and helps to add value and improve organizational value.
- By having robust internal controls in place, organizations can demonstrate to auditors that they have taken proactive measures to safeguard their assets and prevent financial misstatements.
- They review the accounting policies, estimates, and disclosures to ensure they are in line with the required standards.
- In some cases, an organization may outsource its internal audit function and, when this occurs, it should function no differently than if carried out by employees.
- These capabilities allow analysts to focus on critical tasks such as audit preparedness, adjustments, and reporting.
It provides valuable insights, helps ensure compliance, and contributes to an organization’s overall success and sustainability. Small businesses often think that audits are only for large corporations, but this is a misconception. Internal audits, especially when coupled with accounting services for small business, can provide valuable insights into cash flow management, operational efficiency, and risk assessment.
Regulatory Requirements and Standards
- For example, an external auditor might confirm inventory valuation or assess allowance for doubtful accounts.
- Individuals aspiring to be external or internal auditors can jump-start their careers or advance their knowledge with a bachelor’s degree in accounting.
- Their expertise and experience in forensic accounting enable them to identify irregularities or suspicious activities that internal controls may have overlooked.
- This enhances stakeholders’ confidence in the organization’s financial health and performance.
- The benefits of internal audit include having a reporting line within the organisation, being closer to stakeholders, developmental opportunities beyond audit, representation and impact on the business.
An internal auditor is responsible to the organization, particularly the organization’s upper-level management and regulatory board. Now that we have a clearer idea of what internal vs. external audits are, it may be helpful to more clearly define how these two important processes differ. It’s possible that internal auditors have additional obligations that get in the way of their auditing work. When conducting an internal audit, it is important to verify that you are retained earnings balance sheet following all applicable laws, rules, and industry best practices. While the internal and external audit functions are complementary and may need to work closely together, their purposes and areas of focus differ.

The Importance of Cybersecurity in Auditing Practices in Muscat

Internal auditors are integral to an organization’s internal control system, focusing on assessing and improving risk management, control, and governance processes. They conduct operational audits to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations. For instance, an internal auditor might review the procurement process to ensure compliance with company policies and identify cost-saving opportunities. Their work follows frameworks like the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing, which emphasize objectivity and systematic evaluation. On the other hand, an external audit is performed by independent audit firms or certified public accountants (CPAs) outside of the organization. External auditors are hired by the organization’s stakeholders, such as shareholders, creditors, or government agencies, to provide an unbiased opinion on the accuracy and fairness of the organization’s financial statements.

The Hidden Cost of Shortcuts: Why We Risk It and What It Means for Quality Management
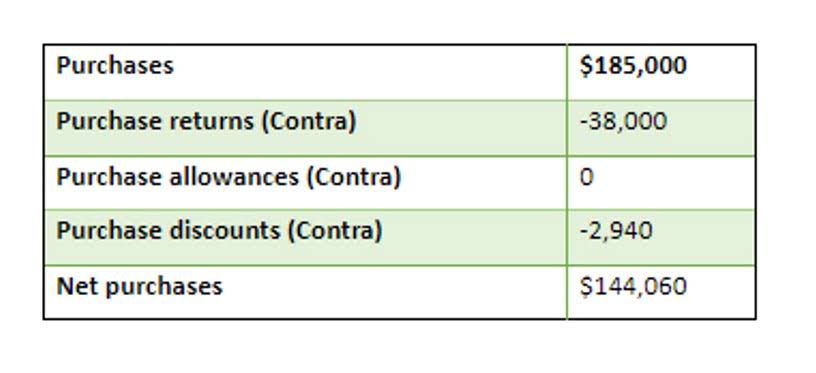
These may include conducting risk assessments, evaluating the adequacy of internal controls, identifying process inefficiencies, and recommending remedial actions to mitigate risks and enhance internal vs external audit operational effectiveness. Internal audit constitutes an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. It aids in accomplishing its objectives by taking a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluating and enhancing the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes. External auditors’ remit is to preserve independence by mitigating organizational influence and maintaining objectivity throughout the audit process.
- The external auditors have never worked with any of the company’s administrators or employers before.
- They provide an unbiased stamp of approval that builds trust and opens doors to new markets.
- Both internal and external auditors contribute to areas like fraud detection and regulatory compliance.
- When it comes to auditing, it’s important to understand the difference between internal and external audits.
- Now that we have a clearer idea of what internal vs. external audits are, it may be helpful to more clearly define how these two important processes differ.
- They may have seen problems similar to your own and have solutions that you might never have thought of.
Scope of External Audits
Internal audits can be conducted to review an organization’s operational activities, and the entity’s management determines the work area. The company decides the scope of an internal audit, but that of an external audit is fixed by law. Since internal auditors may not be certified chartered accountants, they lack the knowledge and experience to Restaurant Cash Flow Management do their work efficiently.